Unfortunately, parasites can live and feed not only in a person's internal organs, but also penetrate under the skin. This causes a number of diseases that have their own specifics. It is important to diagnose the cause of the unpleasant symptoms in time and start treatment before the parasitic worms cause serious damage to the body. Most parasites that live under the skin can only become infected in tropical latitudes: swimming in a stagnant pond, drinking unboiled water, or falling victim to a blood-sucking insect. But some individuals are "installed" in their bodies without leaving their homes.
Varieties of diseases and pests
Medicine distinguishes a number of diseases, the diagnosis of which indicates subcutaneous worms in humans.
- Cysticercosis. Its causative agents are the larvae of pork tapeworms. Most often they enter the body with water or unboiled food. These worms are localized in the internal organs, eyes, brain, muscles and under the skin (they are observed on the shoulders, palms, chest). Such parasites can live in a person for years, thickenings and swellings form under the epidermis, which thicken over time. The diagnosis is slightly facilitated by urticaria, which is constantly manifested by skin rashes.
- Schistosomiasis. This disease is caused by helminths that live in the waters of Africa and Asia. Worms affect the genitourinary system and the skin. The main symptoms are itching, rashes, dermatitis, profuse sweating at night, kidney damage, liver enlargement.
- Filariasis. They are filiform nematodes living in South America, Asia and Africa. They are spread by blood-sucking insects. The disease develops for a very long time (up to seven years), but causes a number of skin pathologies: ulcers, eczema, nodes, papules, rashes. If a person does not pay attention to constant headaches, drowsiness, sleep disturbances and general weakness, complications can develop in the form of arthrosis, glaucoma, cataracts.
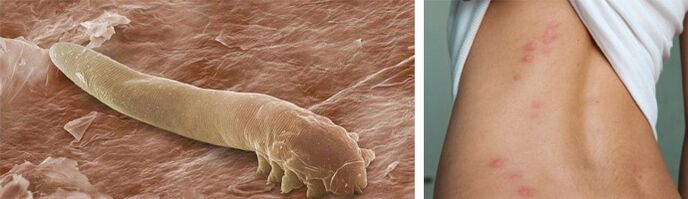
- Scabies. The scabies mite half a century ago was quite common. It settles in the deep layers of the epithelium, feeds on it and lays eggs there. The female parasite lives for about two months, but manages to lay several dozen eggs under the skin. The tick passes through passages in the epithelium, and this is what causes severe itching. Places of localization - folds on the body, sides of the thighs, mammary glands, armpits, genitals and hair. Human skin is covered with rashes, pimples, boils, and other complications arise.
- Dirofillaria. These are parasites that can exist not only subcutaneously, but also affect the eyeball. Females of these worms reach a length of up to 30 cm, and males - up to 10. Carriers of worms of this species are dogs and cats, and biting them, mosquitoes transmit microfilariae larvae tothe man. In this case, the development of an adult in the body may take years. According to statistics, most of the removal of eyeballs falls precisely on the diagnosis of dirofillaria, after a complete deterioration of vision, up to blindness. Seals form under the skin, which itch, turn red and can grow to the size of an egg. It is in them that the adult worm is located.
- Dracunculiasis (guinea worm). These are roundworms, reaching a length of up to 120 centimeters. More common in tropical climates. Besides humans, cats and dogs are also affected. You can get infected with it by drinking unboiled water, swimming in polluted reservoirs. Once in the body in the form of a larva, the worm reaches adulthood only after a year of life in a person. Most often, the legs suffer from this disease: it is they that are prone to complications such as the development of contractures, inflammation of the joints. In addition, the presence of Guinea worm inside a person is fraught with gangrene and blood poisoning.
- Ankylostomiasis. The causative agents of the worms live in places with a tropical and subtropical climate. Hookworms are introduced under the skin of a person through the slightest damage to the skin (usually the legs), and there they remain to parasitize. The disease is manifested by such symptoms as severe itching, sometimes coughing, anemia, signs of damage to internal organs.
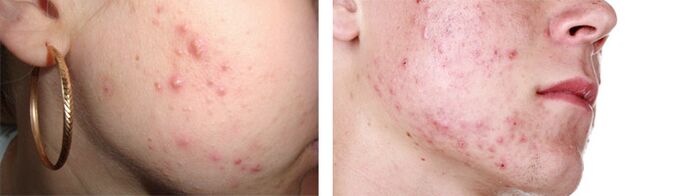
- Demodicosis. It is one of the most common skin conditions. This happens due to the penetration of the tick-causing subcutaneous agent. This is a non-helminthic disease, but the pest also lives in the layers of the epidermis (in the meibomian ducts and sebaceous glands). Symptoms of parasites: abundant and pronounced acne on the face, cheeks, forehead and around the eyes, sometimes there is a loss of eyelashes.
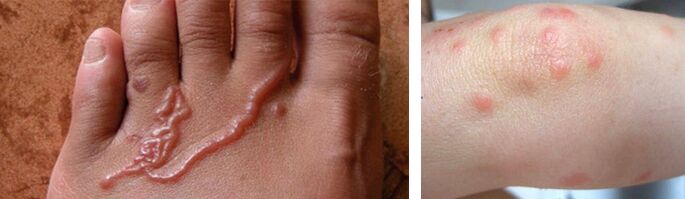
Diagnosis, symptoms and signs
If subcutaneous worms and parasites are suspected, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since some individuals live in humans for several years before "pleasing" the symptoms. Therefore, at the time of detection, pests already have time to harm health.
Since the clinical picture of worms and other subcutaneous inhabitants is rather ambiguous, and many symptoms appear individually, there is usually no unambiguous list of signs. A number of indicators can indicate subcutaneous parasites: constant itching, skin irritation, seals of different sizes, rash, small blisters on the surface of the epithelium, indirectly - sleep disturbances, fatigue. To find out the etiology of such manifestations and exclude helminthic invasion, you need to consult a number of specialists, among them:
- dermatologist;
- neuropathologist;
- allergist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- psychologist (if previous specialists did not find pathologies in their profile).
The diagnosis takes place in several ways, depending on the symptoms:
- blood test for antigens;
- examination of the epidermis sample;
- defame;
- take a secret;
- scraping.
It is these indicators that can detect the presence or absence of parasites on a person's skin.
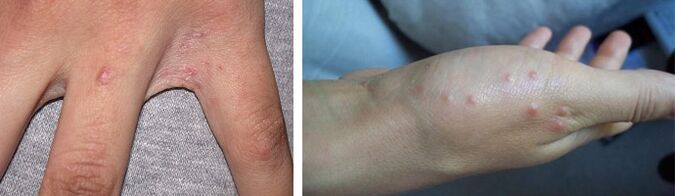
Traditional methods of pest control
The treatment directly depends on the type of parasitic worm. In each individual case, an appropriate therapy is selected, taking into account the age and neglect stage of the problem. Most drugs are quite toxic not only to the worm, but also to the human body.
- getting rid of dracunculiasis is possible only by surgical operation;
- the scabies parasite is effectively expelled by hydrochloric acid and sulfuric soap;
- with schistosomiasis, antimony medication will help;
- the body is rid of demodicosis by a cosmetic line for the care of the skin of the face (special soap for washing, cream).
Along with traditional drug treatment, the patient should strengthen hygienic procedures, carefully monitor the cleanliness of the body, premises, clothes and avoid unnecessary contact with people. In some cases, you will need diet food, cosmetics for skin care.
Prevention of subcutaneous worms
With helminthic invasions, you need to be extremely careful, because it is quite simple to settle parasites in the body, and it can take years for a correct diagnosis and cure.
In order to minimize the risk of infection with subcutaneous worms, doctors advise to remember the following rules:
- before traveling to countries with a tropical climate, you must be vaccinated;
- always respect the rules of hygiene: wash your hands after contact with a large number of people, money, after going to the toilet, before eating;
- women should not use someone else's cosmetics, as there is a high risk of getting parasite larvae (or a tick) on their skin;
- fruits and vegetables should be thoroughly washed before use, but it is better to pour boiling water, subject the meat to prolonged thermal effects, boil water for drinking;
- carefully treat any skin lesions with antiseptics, especially in the tropics;
- do not swim in dirty and questionable waters.
If the parasites have settled under the skin, this is a reason to contact a dermatologist as soon as possible. He will be able to determine the type of worm and prescribe adequate treatment. In most cases, the patient is waiting for conservative treatment, including taking anthelmintic drugs and other drugs that relieve the symptoms of the disease in humans.